Evaluation of Disinfectants
Disinfectants are evaluated for their efficacy. Liquid disinfectants are evaluated by suspension test. Suspension tests are either phenol coefficient test or use dilution test. There are several methods for evaluation of disinfectants:
-
(i) Rideal-Walker test (phenol coefficient test).
(ii) Use dilution test.
(iii) Chick-Martin test.
(iv) Kelsey-Sykes test.
(v) Nephelometric method.
(vi) Counting method.
(vii) Zone of inhibition method or disk diffusion method.
(i) Rideal-Walker Test
This procedure is suitable for testing disinfectants miscible with water and showing their antimicrobial action in a manner similar to phenol. The test organism in this method is special strain of either salmonella typhi or staphylococcus aureus.
Firstly, the bacterial culture is prepared in agar slant in culture tubes. Then subculturing can be made into liquid broth medium and incubated at 38°C for 24 hours.
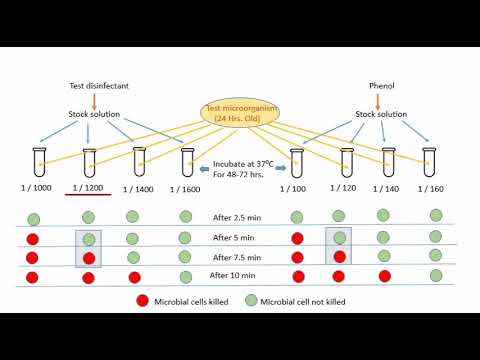
A 5% W/V stock solution of phenol is prepared and further 5 dilutions are prepared (1:100, 1:120, 1:140, 1:160).
Test dilutions of unknown disinfectant are prepared by dissolving 5 ml of unknown disinfectant into 500 ml of sterilized water and further dilutions are made (1:1000, 1:1200, 1:1400, 1:1600).Dilutions of phenol and unknown disinfectant are placed in culture tubes at 20°C. After adding 0.5 ml of 24-hour-old broth culture into each tube, at intervals of 2.5, 5, 7.5 and 10 min, samples are removed and subcultured.
The tubes are incubated and checked for microbial growth. A table is prepared showing which dilution kills the organism and which does not.

| Dilutions | 2.5 min | 5 min | 7.5 min | 10 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disinfectant 1:1000 | + | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1:1200 | + | + | 0 | 0 |
| 1:1400 | + | + | + | 0 |
| 1:1600 | + | + | + | + |
| Phenol 1:100 | + | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1:120 | + | + | 0 | 0 |
| 1:140 | + | + | + | 0 |
| 1:160 | + | + | + | + |
just taking as an example from values mentioned above Higher dilution of disinfectant killing bacteria in 7.5 min but not in 5 min = 1200 Higher dilution of phenol killing bacteria in 7.5 min but not in 5 min = 120 Thus
Means the test disinfactatnt is 10 times more effective then phenol.
Advantages
-
(i) It is inexpensive and can be performed quickly.
(ii) It is reproducible.
Disadvantages
-
(i) It require a sophisticated laboratory.
(ii) Temperature, tissue toxicity and presence of organic matter affect the result.
(ii) Use Dilution Test
It is important that a disinfectant should still be effective when diluted for use. This method is designed.
in a way to study the higher dilution point at which any particular disinfectant exert its effect. Three strains of bacteria are used in this test are staphylococcus aureus, salmonella choleraesuis and Pseudomonas auriginosa. These organisms are cultured in liquid media. Standardised metal rings are dipped in these culture for a specific time and then each of these metal ring is separately dipped into different dilutions of test disinfectant for a specific time and removed. Following this exposure the disinfectant metal rings are again placed in culture media to observe the growth of organism. If any metal ring shows microbial growth when placed in culture media, it can be said that disinfectant is not able to kill microorganism in that particular dilution and the effectiveness of the disinfectant is then determined by the number of organisms present in culture.(iii) Chick-Martin Test
The presence of organic matter affects the activity of disinfecting agent.
Thus, this method can evaluate the activity of disinfectant in presence of organic matter. Dried yeast is used as organic matter. The test is conducted by inoculation of Salmonella typhi into solution containing different dilution of test disinfectant and phenol as standard. This system of test is kept at 20°C for 30 minutes. Then subculturing is made into culture medium and incubated the inoculated culture at 37°C for 48 hours. The subculturing is made into duplicate and observe the growth of organism. The concentration of phenol and test disinfectant that prevent the growth of organism is determined and coefficient is calculated by dividing the value of phenol by value of disinfectant.

(iv) Kelsey-Sykes Test
This method involves four strains are S. aureus, E. coli, P. auriginosa and Proteus vulgaris.
The methodology is same as with Chick-Martin test but in this method, no standard solution is established and the method is carried out in the presence of tween 80 instead of dried yeast. Thus, this method does not provide data about efficacy, but reports only the data of pass or fail for any disinfectant.(v) Nephelometric Method
In this method the determination of bacteria can be done by using a nephelometer.
Nephelometric method is used to evaluate the effectiveness of a disinfectant by measuring the turbidity (cloudiness) produced in a bacterial suspension. When disinfectant starts killing the microorganisms, the bacterial cells get lysed and the turbidity of the suspension decreases. A nephelometer measures this change in turbidity by detecting the amount of light scattered by the bacterial cells in the suspension. If the disinfectant is highly effective, the turbidity will drop quickly because most bacteria are killed. By comparing the turbidity reading before and after adding the disinfectant, we can determine how powerful and how fast the disinfectant works. This method is quick, simple, and useful for comparing the germicidal activity of different disinfectants.(vi) Disk-Diffusion Method
This method is used in laboratories to evaluate the efficacy of chemical agent.
In this method a filter paper of a fixed dimension is soaked with a disinfectant and placed on an agar plate that has been previously inoculated and incubated with test organism. If the disinfectant is effective, then after incubation a zone of inhibition is formed around the filter paper which is placed in agar medium. The efficacy of any disinfectant can be determined by measuring the diameter of zone of inhibition. Fomation of zone of inhibition indicate that the test disinfectant is effective against microorganism, and the diameter of zone of inhibition indicate that how much the test disinfectant is effective against the selected microorganism. More the diameter of zone of inhibition, higher the effectiveness.